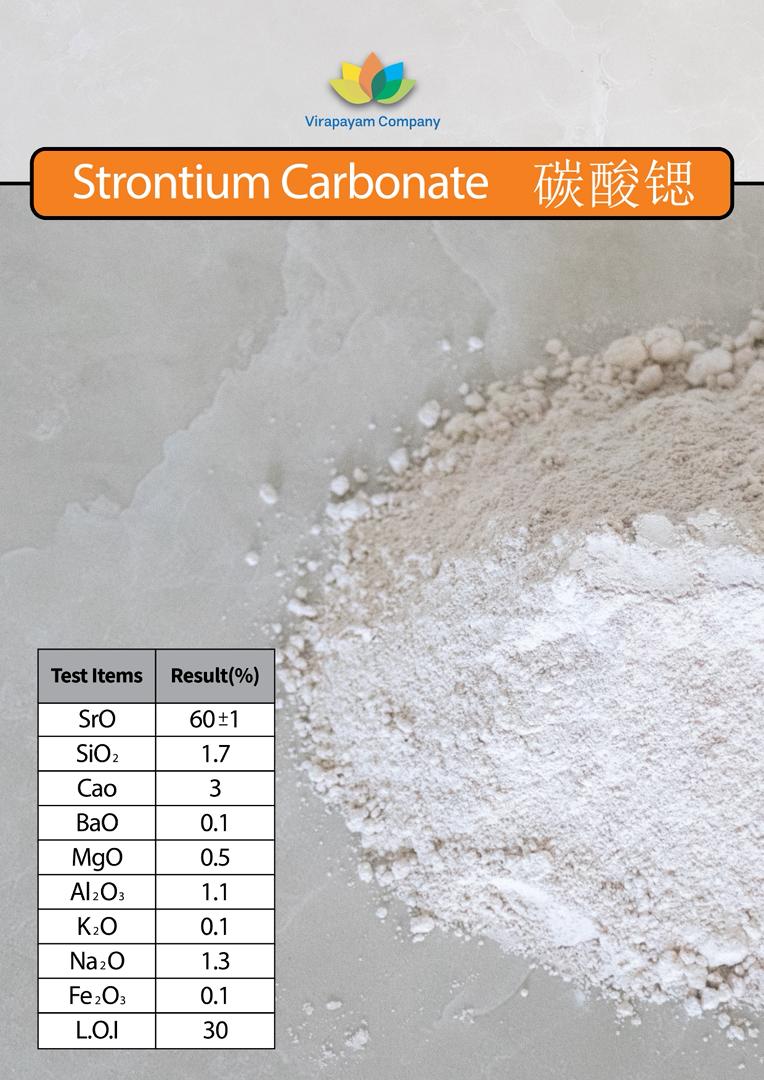
🌟 Strontium Carbonate (SrCO₃): The Quiet Force Beneath the Surface 🌍⚪
Strontium Carbonate is a naturally occurring white crystalline compound that forms the foundation for a wide array of transformative industrial processes. While its chalky-white appearance may seem unassuming, this mineral holds an extraordinary place in the intersection of geology, chemistry, and high-tech manufacturing. Derived from the earth yet purified to near-perfection, it’s both a raw material and a chemical building block, trusted for its reactivity, stability, and structural elegance.
📌 Basic Mineral Profile
- Name: Strontium Carbonate
- Chemical Formula: SrCO₃
- Molar Mass: 147.63 g/mol
- Mineral Group: Carbonates
- Crystal System: Orthorhombic
- Color: White to colorless
- Hardness: ~3.5 (Mohs scale)
- Density: ~3.74 g/cm³
- Luster: Dull to slightly vitreous
- Solubility: Practically insoluble in water, but reacts in acids
- Streak: White
- Melting Behavior: Decomposes to SrO and CO₂ when heated above 1494°C
- Transparency: Translucent to opaque
🌋 Geological Formation & Natural Occurrence
Strontium Carbonate rarely occurs in nature in large deposits but is usually synthesized from celestine (SrSO₄), a more abundant strontium-bearing mineral. In the natural world, it forms in alkaline lakebeds, limestone deposits, and as a result of precipitation reactions in hydrothermal systems. It may also appear as a secondary mineral, forming by alteration of strontium-bearing sulfates.
🌐 Countries with notable strontium resources include:
- Iran
- China
- Spain
- Mexico
- Turkey
- USA
These regions contribute to the global supply chain for a range of advanced manufacturing and specialized processing industries.
🔬 Crystal Chemistry & Reactivity
Strontium Carbonate consists of large Sr²⁺ cations bonded with CO₃²⁻ carbonate anions in an orthorhombic lattice. This configuration results in:
- High thermal stability
- Clean thermal decomposition
- Predictable acid-base behavior
- Strong compatibility with metal oxides
- Ability to act as a precursor in redox transformations
Upon heating, it releases carbon dioxide, leaving behind strontium oxide (SrO) — a transformation essential in several thermochemical pathways. This reaction occurs cleanly, with minimal byproducts, making it ideal for processes that demand purity and efficiency.
⚗️ Purification & Industrial Suitability
Strontium Carbonate can be produced synthetically with extremely high purity levels (≥99.9%) using carbonate precipitation methods. These include:
- Carbonation of strontium hydroxide solutions
- Conversion from celestine via strontium sulfide intermediate
- Ion-exchange and recrystallization techniques for laboratory-grade material
Its purity and predictable behavior in reaction environments make it a key compound in industries where consistency and trace-level control are non-negotiable.
🌟 Why Strontium Carbonate Stands Out
- ✅ Chemically versatile – supports multiple pathways in materials science and metallurgy
- ✅ Environmentally stable – safe to store, transport, and process
- ✅ Easy to convert – a gateway to more reactive strontium compounds
- ✅ Compatible with thermal and optical systems – thanks to clean decomposition and refractive properties
- ✅ Industrial-grade and ultra-pure grades available – enabling precision across different technological domains
✨ Marketing Teaser: A Material of Quiet Mastery
"Strontium Carbonate — The White Architect of Industrial Innovation."
From geochemical silence to high-tech impact, this mineral stands as a bridge between Earth's calm and human ingenuity. Behind every reaction it fuels is a history of purity, power, and quiet chemical brilliance.

