🏗️ Gypsum: Industrial & Functional Applications
Gypsum, or calcium sulfate dihydrate (CaSO₄·2H₂O), is a versatile non-metallic mineral used extensively across numerous industries due to its abundance, chemical stability, fire resistance, and binding properties. Below is a categorized breakdown of its applications:
🏠 1. Construction & Building Materials
- Plaster of Paris (POP)
- Created by heating gypsum (calcination)
- Used in interior wall coatings, ceiling molds, decorative elements, and drywall repair
- Drywall / Gypsum Board / Wallboard
- Essential in modern construction for interior walls and ceilings
- Lightweight, fire-resistant, sound-insulating
- Cement Additive (Retarder)
- Added to Portland cement to control setting time
- Prevents flash setting and improves workability
- Gypsum Mortars & Plasters
- Historical use in ancient architecture (e.g., Egyptian pyramids)
- Now used in eco-friendly construction systems

🌾 2. Agriculture & Soil Management
- Soil Conditioner / Amendment
- Improves soil structure by reducing compaction and crusting
- Enhances water infiltration and aeration
- Source of Calcium and Sulfur
- Provides essential nutrients for crop growth (especially in sulfur-deficient soils)
- Reclamation of Sodic / Saline Soils
- Displaces sodium ions and helps restore soil fertility
- Pelletized Gypsum
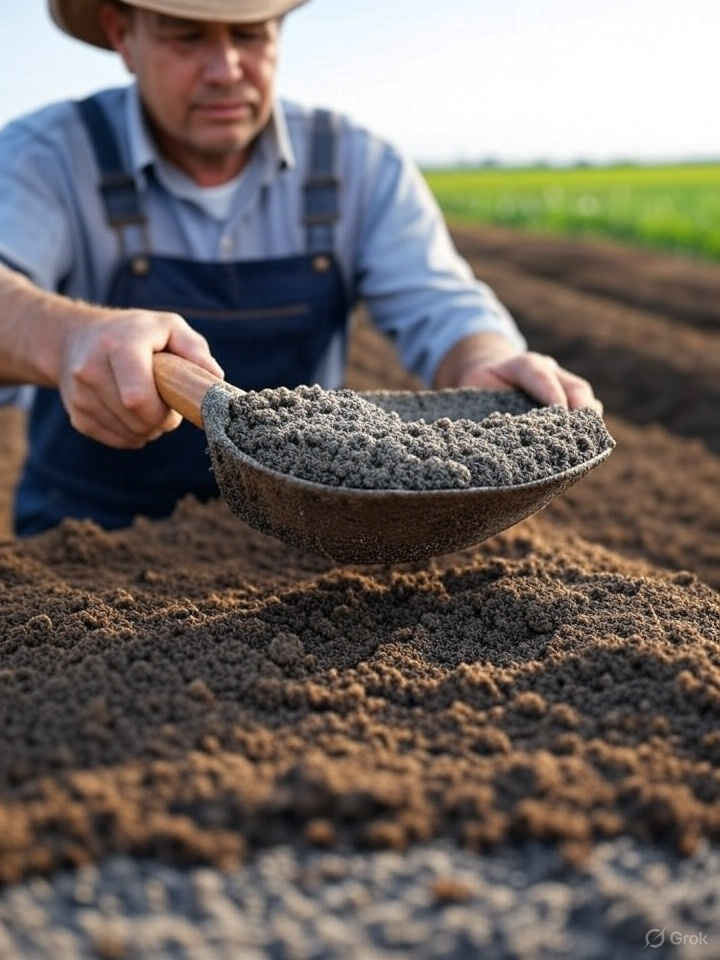

🏭 3. Industrial Processing & Manufacturing
- Mold Making & Casting
- Used in ceramics, glassware, sculpture, and dental molds
- Captures fine detail and sets quickly
- Food & Beverage Industry (Food-Grade Gypsum)
- Coagulant in tofu production
- Added in brewing to adjust water hardness (e.g., "Burtonizing" beer)
- Paint & Coating Filler
- Acts as a whitening agent, extender, and texturizer
- Paper Manufacturing
- Used in gypsum board paper liners and paper finishing
- Textile and Dyeing
- Assists in pigment fixation and dyeing processes

- Assists in pigment fixation and dyeing processes
🧪 4. Chemical Industry
- Sulfuric Acid Production
- In some processes, gypsum is a source of sulfur for H₂SO₄ synthesis
- Calcium Sulfate Derivatives
- Precursor for anhydrite, hemihydrate, and other specialty materials

- Precursor for anhydrite, hemihydrate, and other specialty materials
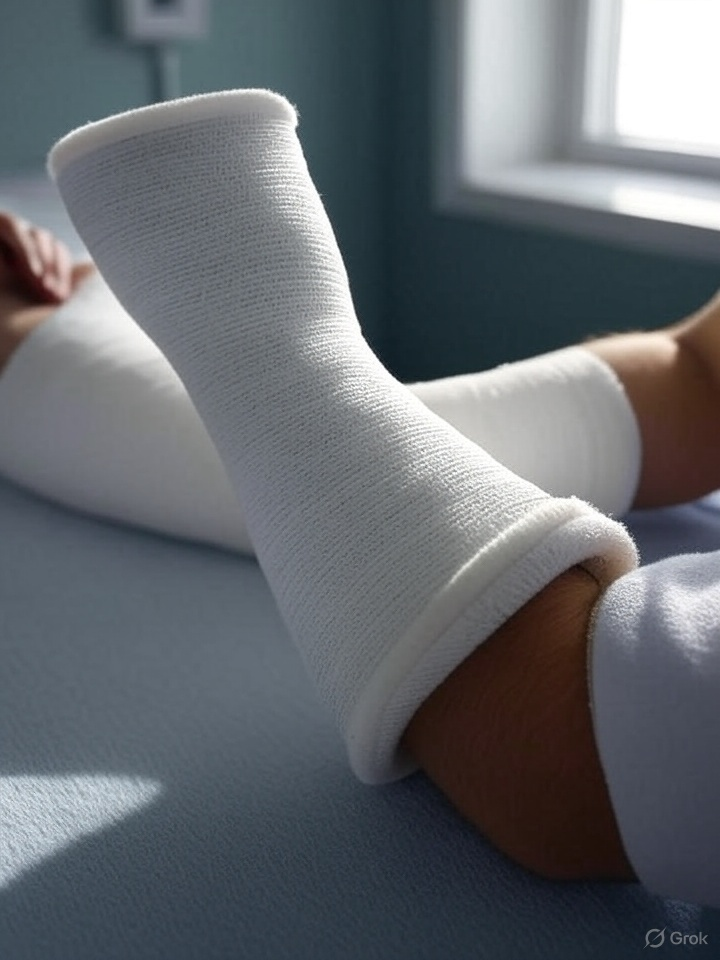
🏥 5. Medical & Healthcare
- Orthopedic Casts & Splints
- Used to immobilize broken bones
- Lightweight, moldable, and sets rapidly
- Dental Applications
- For impressions, study models, and prosthetic moldings
- Surgical Grade Plaster
- Used in prosthetics and rehabilitation devices
- Used in prosthetics and rehabilitation devices
🎨 6. Art, Education & Decorative Use
- Statues and Relief Work
- Preferred for detailed carving and casting
- School and Lab Models
- Educational models for anatomy, geology, and chemistry
- Crafts and DIY Projects
- Safe, inexpensive material for hobbyists and artists

- Safe, inexpensive material for hobbyists and artists
🌿 7. Environmental & Waste Management
- Flue-Gas Desulfurization (FGD) Gypsum
- By-product of power plants’ sulfur dioxide scrubbing systems
- Recycled into drywall or agricultural applications
- Wastewater Treatment
- Gypsum can precipitate phosphates and neutralize alkaline effluents
- Land Reclamation
- Environmental & Waste Management Flue-Gas Desulfurization (FGD) Gypsum By-product of power plants’ sulfur dioxide scrubbing systems Recycled into drywall or agricultural applications Wastewater Treatment Gypsum can precipitate phosphates and neutralize alkaline effluents Land ReclamationApplied in mine tailings and degraded lands to restore productivity
- Applied in mine tailings and degraded lands to restore productivity

🚜 8. Reduces ammonia emissions and improves hygiene
"Reducing ammonia emissions and improving hygiene is possible through the use of materials like gypsum or specific additives in waste and environmental management. This method is particularly useful in livestock farms and industrial facilities where ammonia emissions can be problematic. By absorbing and neutralizing ammonia, it reduces unpleasant odors and creates a healthier environment for animals and workers. Additionally, this process helps maintain air quality and reduce pollution, which is essential for environmental sustainability.
✅ Summary
Gypsum is a low-cost, abundant, and multifunctional mineral used in industries ranging from construction and agriculture to medicine, manufacturing, and environmental restoration. Its
