🎬 "Gypsum: The Hidden Giant Beneath Your Feet!"
🌍✨ Unseen yet essential, Gypsum is the soft, silent architect of nature and industry.
💎🔬 With its crystal clarity, perfect structure, and geologic elegance, this mineral is a key player in Earth’s story — from ancient seas to modern science.
🪨💫 Discover the science behind the softness — Gypsum, nature’s quiet masterpiece.
🧬 1. Chemical Composition and Formula
- Chemical Formula: CaSO₄·2H₂O
- Components:
- 🧪 Calcium (Ca)
- 🔥 Sulfur (S)
- 🌬️ Oxygen (O)
- 💧 Water (H₂O) – Two water molecules → "dihydrate"
🧱 2. Crystal Structure and Physical Properties
🧊 Crystal System:
- Monoclinic – Tabular or prismatic crystals
- Cleavage: Perfect on one plane
- Twinning: Common, often contact twins called "swallowtail twins" 🕊️
📐 Hardness:
- Mohs Scale: 2 – Very soft (scratchable with fingernail)
⚖️ Specific Gravity:
- Around 2.3 – Relatively light
🔎 Transparency:
- Transparent to translucent
🌈 Color:
- Commonly white, but may also appear:
- Gray, red, brown, yellow, or pink (due to impurities) 🎨
💎 Luster:
- Vitreous (glassy) to pearly on cleavage surfaces
🌍 3. Geological Formation and Occurrence
🏞️ Origin:
- Sedimentary – Forms from the evaporation of saline waters in lakes and seas
🧪 Formation Process:
- Water bodies rich in calcium and sulfate ions begin to evaporate 🌞
- Dissolved minerals precipitate out
- Gypsum crystallizes early in the evaporite sequence 🧂
🗺️ Common Locations:
- Found worldwide, especially in:
- 🇺🇸 USA (Oklahoma, Iowa)
- 🇲🇽 Mexico
- 🇮🇷 Iran
- 🇪🇸 Spain
- 🇨🇳 China
- 🇨🇦 Canada
🧫 4. Types and Varieties of Gypsum
- ✨ Selenite
- Clear, colorless crystals
- Transparent and often striated
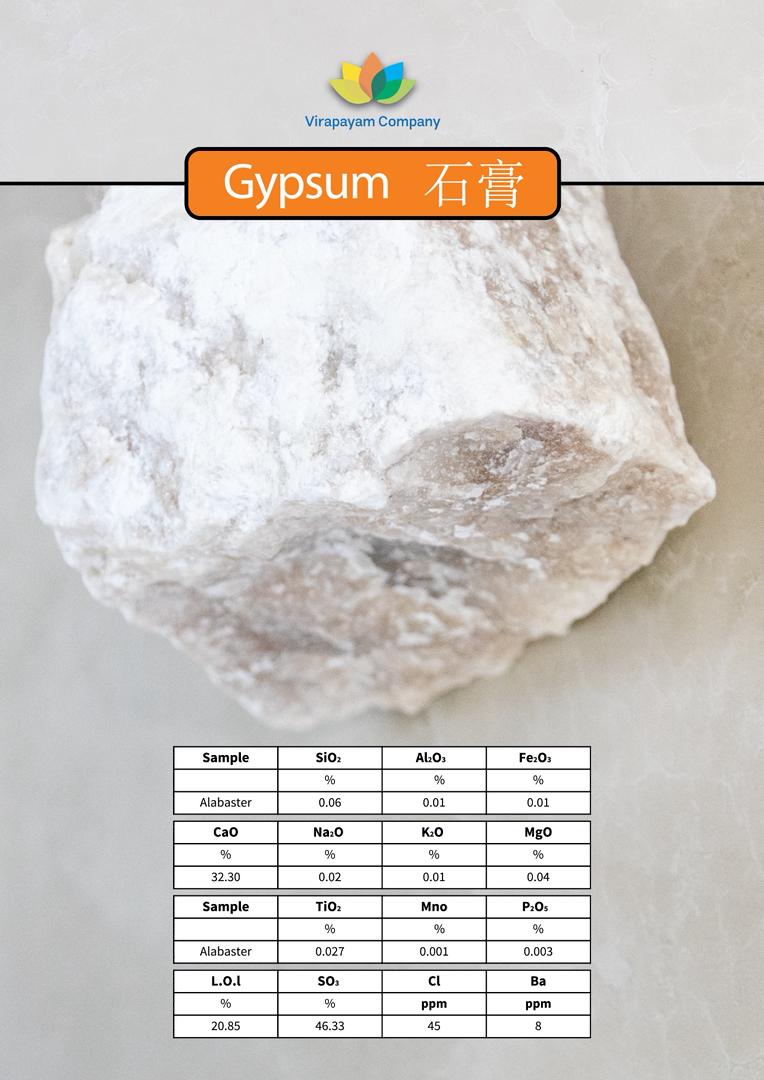
- 🗿 Alabaster
- Fine-grained, white to pale-colored
- Commonly used for carving (though not covering uses here)
- 💫 Satin Spar
- Fibrous form
- Silky sheen with chatoyancy (cat’s eye effect)
- 🌹 Desert Rose
- Rosette-shaped clusters of tabular crystals
- Typically found in arid climates
🔁 5. Stability and Transformations
- 🔥 Dehydration:
Heated to ~150°C → loses water → forms Plaster of Paris (CaSO₄·½H₂O) - 💧 Rehydration:
Can absorb water and revert to gypsum - 🌋 Anhydrite Formation:
At higher temperatures/depths → converts to anhydrite (CaSO₄)
📖 6. Identification Tips
- ✋ Very soft – scratches with fingernail
- ⚖️ Low specific gravity
- 📏 One perfect cleavage
- 🚫 Does not react with HCl acid (unlike calcite)
🧪 7. Chemical Reactions and Behavior
- ⚖️ Stable in neutral environments
- 💧 Slightly soluble in water (~2.0–2.5 g/L at 25°C) 🌡️
- 🧾 Forms sulfate ions in solution
- 🧫 Acts as a source of calcium and sulfur in geochemical systems
🧭 8. Environmental Role
- ✅ Non-toxic
- 🌱 Contributes to soil structure and chemical balance
- 🌊 Involved in evaporite basin development

